|
Most of the site will reflect the ongoing surgical activity of Prof. Munir Elias MD., PhD. with brief slides and weekly activity. For reference to the academic and theoretical part, you are welcome to visit
neurosurgery.tv
Functional Neurosurgery
functionalneuro.surgery
Functionalneurosurgery.net
IOM Sites
iomonitoring.org
operativemonitoring.com
Neurosurgical Sites
neurosurgery.art
neurosurgery.me
neurosurgery.mx
skullbase.surgery
Neurosurgical Encyclopedia
neurosurgicalencyclopedia.org
Neurooncological Sites
acousticschwannoma.com
craniopharyngiomas.com
ependymomas.com
gliomas.info
gliomas.uk
meningiomas.org
neurooncology.me
pinealomas.com
pituitaryadenomas.com
Neuroanatomical Sites
humanneuroanatomy.com
microneuroanatomy.com
Neuroanesthesia Sites
neuro-anesthessia.org
Neurobiological Sites
humanneurobiology.com
Neurohistopathological
neurorhistopathology.com
Neuro ICU Site
neuroicu.info
Neuroophthalmological
neuroophthalmology.org
Neurophysiological Sites
humanneurophysiology.com
Neuroradiological Sites
neuroradiology.today
NeuroSience Sites
neuro.science
Neurovascular Sites
vascularneurosurgery.com
Personal Sites
cns.clinic
Spine Surgery Sites
spine.surgery
spondylolisthesis.info
paraplegia.today
Stem Cell Therapy Site
neurostemcell.com

Inomed Stockert Neuro N50. A versatile
RF lesion generator and stimulator for
countless applications and many uses

Multigen RF lesion generator .
|
 |
|
 |
| |
|
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) describes a group of
syndromes caused by pathological processes predominantly
affecting the frontal and temporal lobes. It
represents the most frequent cause of non-AD
degenerative
dementia and has been increasingly recognized as an
important cause of early-onset dementia.
At least three major anatomic variants of FTD can be
described: a bifrontal, slightly asymmetric subtype with
more involvement of the right frontotemporal region
(frontal variant), a temporal-predominant subtype
(temporal variant or semantic dementia), and a left
frontal-predominant subtype (progressive nonfluent
aphasia). There is clinical and pathological
overlap
between the syndromes and the influence of genetic
factors varies substantially across the syndromes.
Symptoms can be generally related to impairment of
functions of the affected brain regions, with behavioral
symptoms and deficits in executive functions.
Extensive loss of pyramidal neurons in the
frontotemporal
cortex, severe gliosis within the gray and white
matter, and presence of Pick bodies are the most common
histologic findings.
Structural MRI scans frequently reveal frontal lobe
and/or anterior temporal lobe atrophy, often with
significant
asymmetry. When advanced volumetric
techniques such as voxel-based morphometry are
used, brain atrophy in the different types of FTD
seem to be closely correlated to the cerebral location
responsible for the clinical syndrome. It
has been suggested that it may be possible to
differentiate
autopsy-proven FTD from AD on the basis of
the brain atrophy pattern. However, at the earliest
disease stages, the differential diagnosis between
dementia types is difficult, even using quantitative
neuroimaging techniques.
1H-MRS
The metabolite changes of FTD patients are very similar
to those seen in AD. Usually, NAA/Cr
is lower than in normal controls and mI/Cr is higher. However, accurate regional 1H-MRS measurements
may help to differentiate dementias that display
regionally specific involvement such as FTD.
This may be particularly important at the early stages
of disease progression, as these regional differences
may disappear at later stages when the neurodegenerative
pathology becomes more widespread and
involves the majority of the cerebral cortex. |
|
|
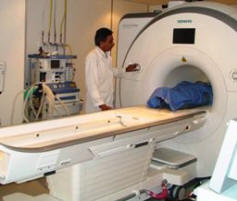 Skyra MRI with all clinical applications in the run since 28-Novemeber-2013.

Leica HM500
The World's first and the only Headmounted Microscope.
Freedom combined with Outstanding Vision, but very bad video recording and
documentation.

After long years TRUMPF TruSystem 7500 is running with in the neurosuite at
Shmaisani hospital starting from 23-March-2014 |







